
Understanding Connected Load Vs Demand...
January 2, 2026
Building Information Modelling (BIM) is a process that involves creating and managing digital representations of physical and functional characteristics of buildings and infrastructure. BIM models can be used for various purposes, such as design, engineering, construction, operation, and maintenance. However, not all BIM models are the same. Depending on the project scope and requirements, different types of BIM models may be needed. In this newsletter, we will compare two common types of BIM models: Construction BIM and Design BIM, with a focus on Mechanical, Electrical, and Plumbing (MEP) and Fire Protection (FP) models. We will also discuss the areas to be considered while working on these models and the expertise required for both.
Construction BIM models are created by contractors or subcontractors to support the construction process. They are typically derived from the design or engineering models provided by the architects or engineers, but they may also include additional details, such as fabrication, installation, coordination, and sequencing information. Construction BIM models are used for tasks such as clash detection, quantity take-off, scheduling, site logistics, and safety analysis. Construction BIM models are usually more detailed and accurate than design or engineering models, as they reflect the actual conditions and specifications of the project.
Design BIM models are created by architects or engineers to support the design or engineering process. They are typically based on the client’s requirements, codes, standards, and best practices. They may also include analysis, simulation, and optimization information. Design BIM models are used for tasks such as conceptual design, schematic design, design development, documentation, and coordination. Design BIM models are usually more conceptual and abstract than construction models, as they represent the intended design or engineering solutions for the project.
Construction BIM and Design BIM differ in several aspects, such as level of detail, level of development, software, and file formats. The table below summarizes some of the main differences between the two types of models, with a focus on MEP and FP models.
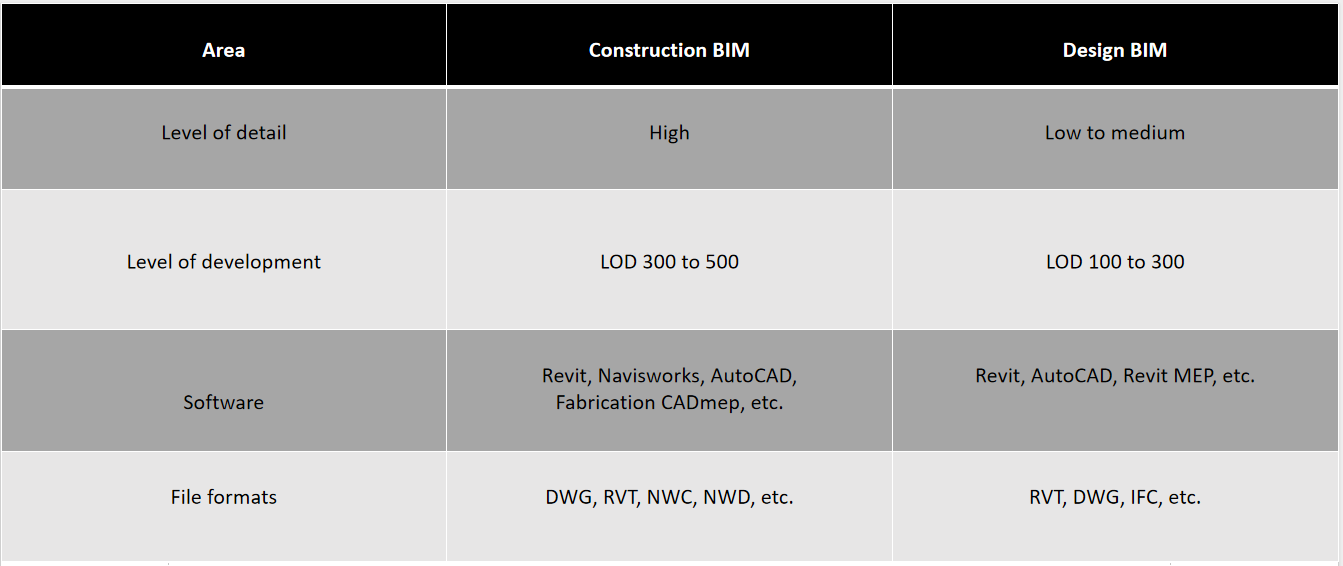
Level of detail (LOD) is a measure of the amount of information and geometry that a model contains. It ranges from LOD 100 (basic) to LOD 500 (as-built). Level of development (LOD) is a measure of the reliability and completeness of a model for a specific purpose. It ranges from LOD 100 (conceptual) to LOD 500 (fabrication and assembly).
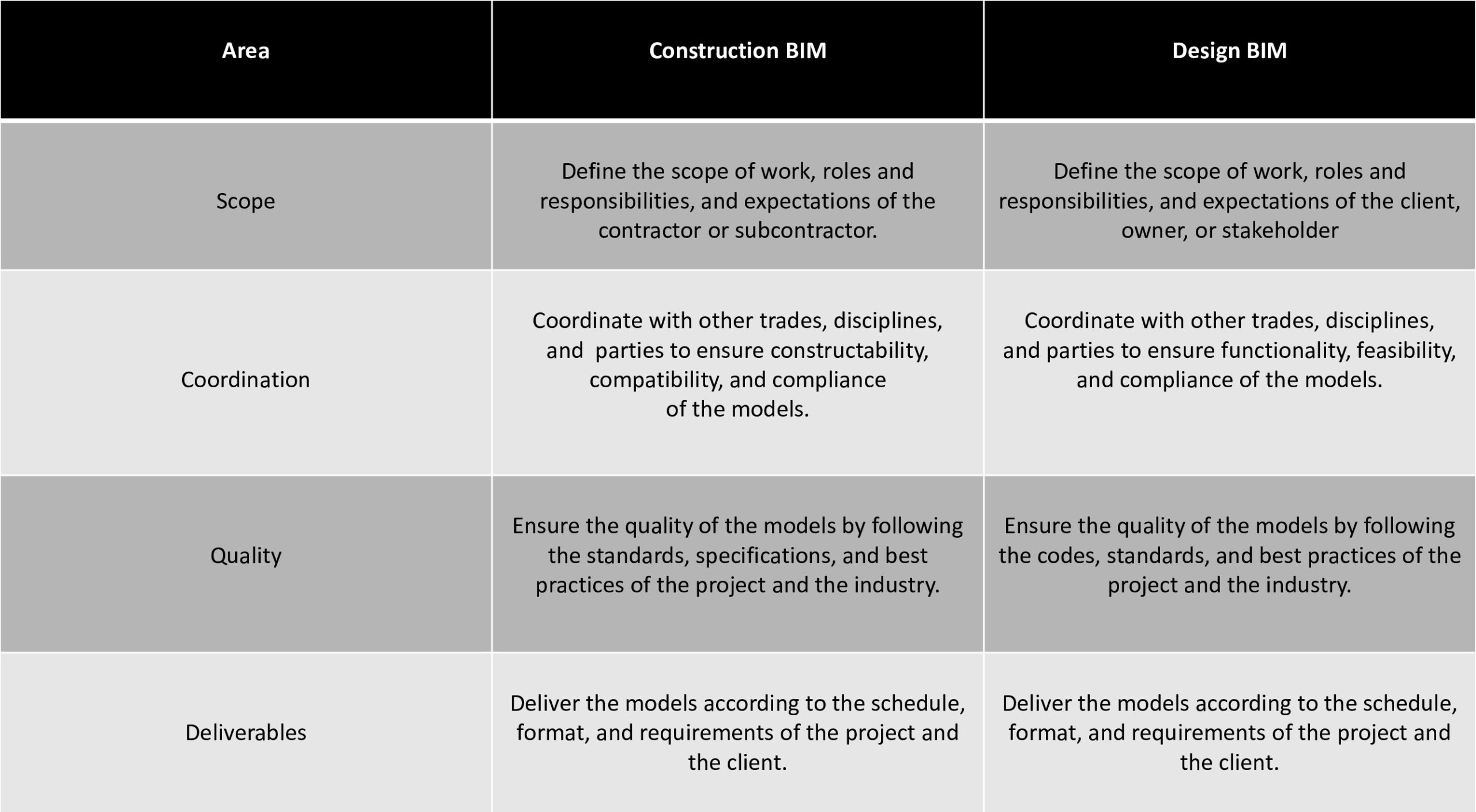
While working on Construction BIM and Design BIM, there are several areas to be considered, such as scope, coordination, quality, and deliverables. The table below outlines some of the key considerations for each area, with a focus on MEP and FP models.
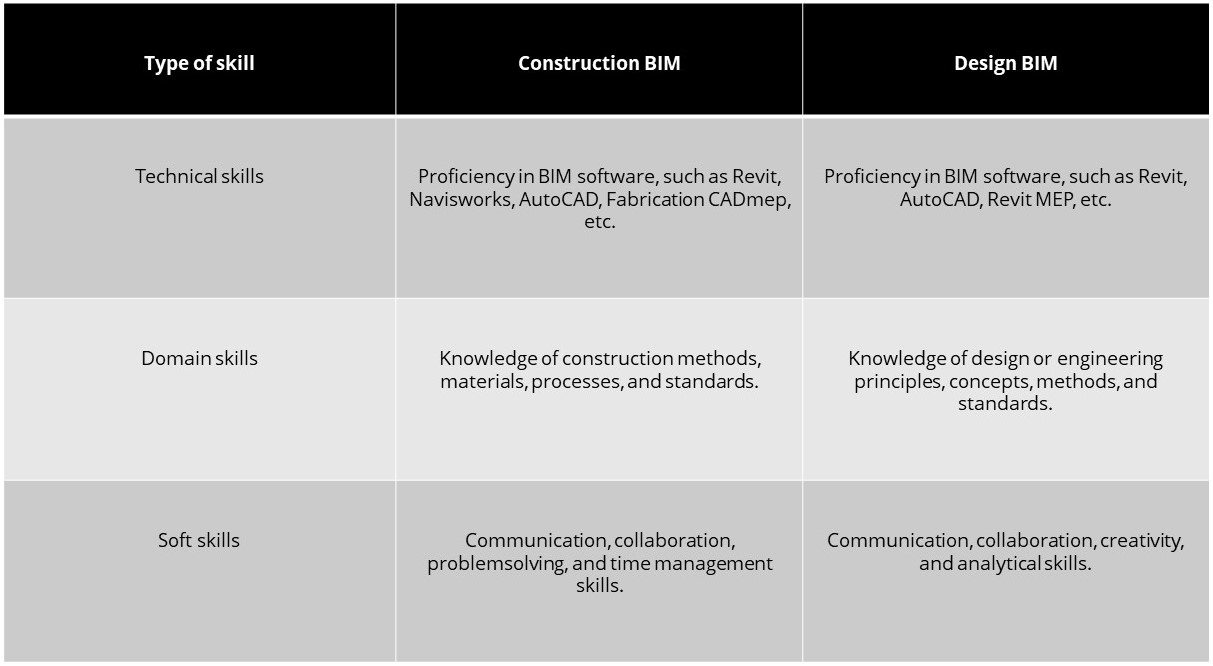
To work on Construction BIM and Design BIM, different types of expertise are required, such as technical, domain, and soft skills. The table below lists some of the common skills required for each type of model, with a focus on MEP and FP models.
In conclusion, Construction BIM and Design BIM are two different types of BIM models that serve different purposes and require different considerations and expertise. By understanding the differences and similarities between them, you can choose the right BIM model for your project and work on it effectively and efficiently.