
Understanding Connected Load Vs Demand...
January 2, 2026
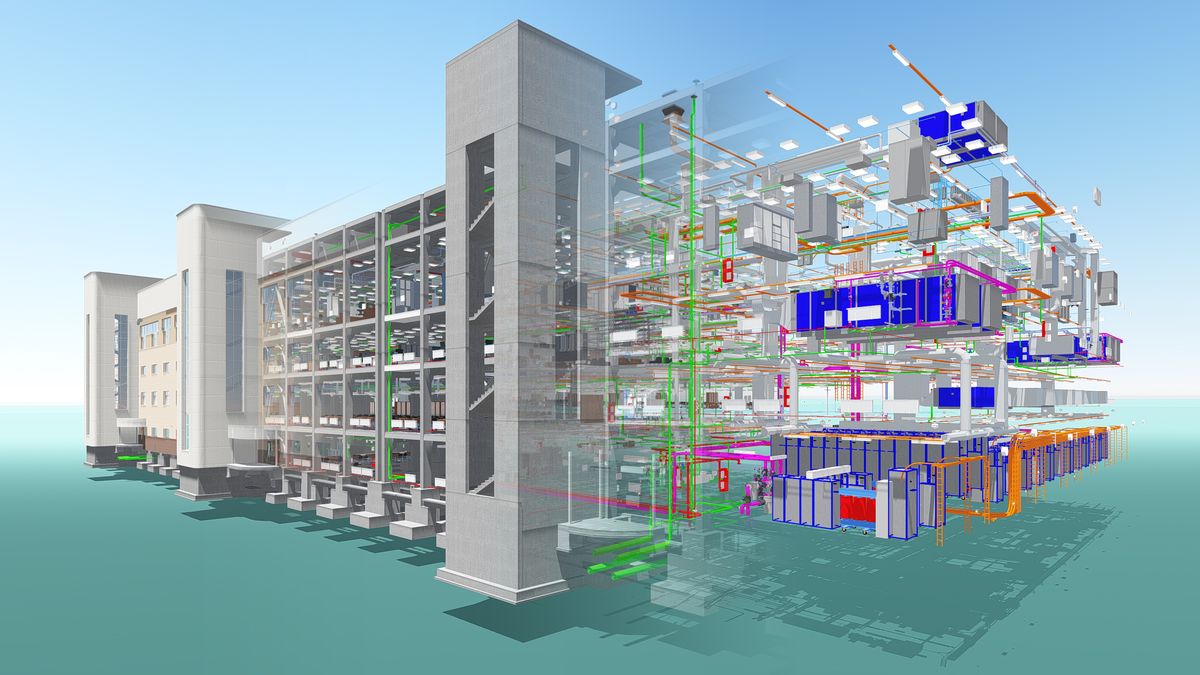
In the world of BIM design and construction, precision is everything. A well-coordinated model ensures seamless collaboration across disciplines, minimizes errors, and streamlines workflows. In Autodesk Revit, project coordinates play a pivotal role in achieving this precision. They define the spatial relationship between various elements in a project and connect the digital model to real- world site data.
Skillful management of project coordinates allows you to tackle even the most complex, cross- discipline construction projects with ease. However, even a small, unnoticed shift in model coordinates can lead to inaccurate clash detection results. In more severe cases, such errors can cause models to completely misalign during assembly, leading to significant challenges in project execution. This blog dives into the significance of these critical points, exploring their roles, interconnections, and best practices for managing them in your Revit projects. Whether you’re a beginner or an experienced professional, understanding these fundamentals will empower you to take control of your project’s coordination and elevate the quality of your work.
In Autodesk Revit, there are several essential concepts for managing project coordinates and ensuring accurate collaboration and alignment between various project files. Here’s an explanation of each:
1. Internal Origin (IO)
2. Project Base Point (PBP)
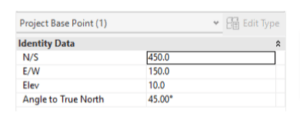
3. Survey Point (SP)
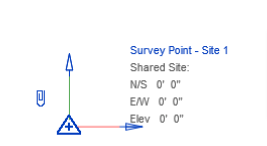

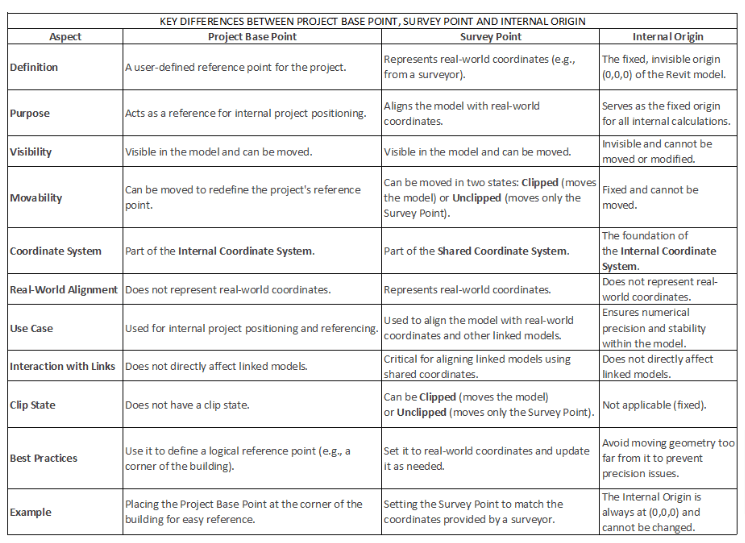
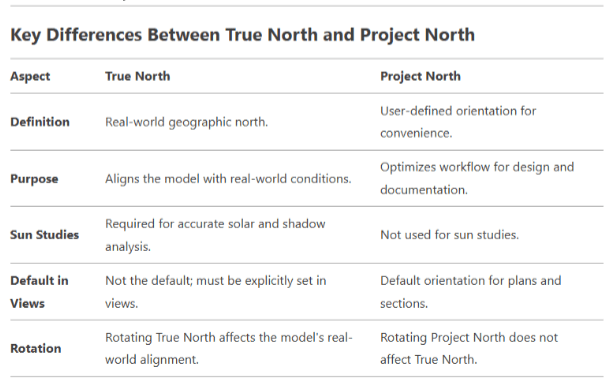
4 . True North and Project North
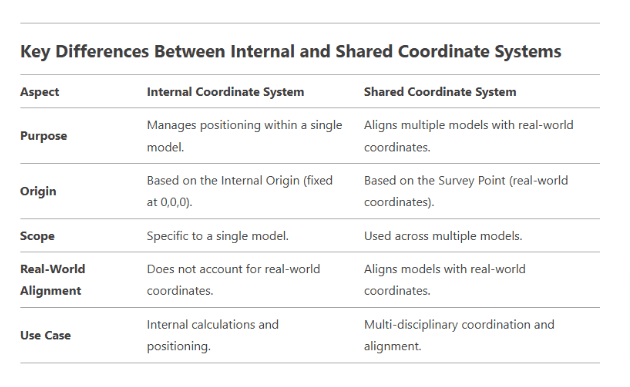
In Revit, coordinate systems are fundamental for positioning and aligning models. Two key concepts are the Internal Coordinate System and the Shared Coordinate System
1. Internal Coordinate System:
The Internal Coordinate System is the default coordinate system in Revit, based on the internal Origin. It is used for all internal calculations and positioning within a single model.
2. Shared Coordinate System:
The Shared Coordinate System is a common coordinate system used to align multiple models (e.g., architectural, structural, MEP). It is based on real-world coordinates and ensures that all models are positioned consistently.
When you link models using shared coordinates, Revit aligns them based on the Shared Coordinate System while maintaining their internal coordinate systems.
Starting a new BIM project with separate architectural, structural, and MEP models requires careful
planning to ensure accurate positioning and coordination. By making the architectural model the
base file for coordinates, you can establish a consistent reference point for all disciplines.
1. Single Source of Truth:
2. Consistency Across Models:
3. Early Setup:
4. Communication:
1. Define the Project Base Point and Survey Point:
2. Set True North:
3. Publish Coordinates:
1. Open the Structural or MEP Model:
2. Link the Architectural Model:
3. Acquire Coordinates:
1. Check Levels and Grids:
2. Check Positioning:
1. Reload Linked Models:
2. Communicate Changes:
1. Use Shared Coordinates:
2. Avoid Moving the Survey Point Unnecessarily:
3. Use Copy/Monitor for Key Elements:
4. Document the Coordinate System: