
Understanding Connected Load Vs Demand...
January 2, 2026

In the event of a fire, quick access to water is crucial for saving lives and minimizing property damage. Standpipe systems, often integrated with fire hose reels, provide the means to rapidly deliver water throughout a building, enabling firefighters to tackle fires effectively and efficiently. Whether in high-rise buildings, industrial facilities, or commercial spaces, standpipe systems are an
essential part of any fire protection strategy.
In this post, we will explore the purpose, components, types, classes, and installation requirements for standpipe systems, while also referencing important building codes.
A standpipe systems primary goal is to provide a reliable water source for firefighters, reducing the need for them to carry and connect long hoses during an emergency. These systems are designed to distribute water to various floors of a building, ensuring that firefighters can quickly and easily access water, even in hard-to-reach areas.

Fire Hose Reels are often integrated with standpipes. These reels allow building occupants or trained personnel to control the water flow and fight small fires before professional responders arrive.
A standpipe system consists of a network of pipes, valves, hose connections, and other equipment that distributes water to designated areas within a building. It provides an essential water supply during fires, helping to control fires, protect life, and reduce structural damage. The water source for
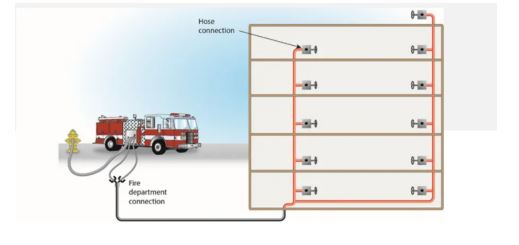
these systems may come from municipal water supplies, on-site storage tanks, or booster pumps.
As defined by NFPA 14 (National Fire Protection Association, 2003), a standpipe system is a fixed arrangement of pipes and components that allow water to be discharged through hoses at various points within a building. The water supply can be constant or activated when needed, depending on the type of system installed.
The classification of standpipe systems is primarily based on when water is available and at what pressure. These include:
Standpipe systems are classified according to the type of hose connections provided and the intended user.
Each class of standpipe system has different flow and pressure requirements, ensuring that firefighters can efficiently use the system for suppression efforts.
Correct pipe sizing is essential to ensuring that water is delivered with the required pressure and flow rate to all parts of a building. Here are some key points regarding pipe sizing:
When calculating the necessary water flow and pressure for a standpipe system, consider the building’s size, occupancy, and specific system classification. For example, in a building less than 80,000 square feet with a Class I system, the flow rate should be calculated as follows:
The installation of standpipe systems must comply with local building codes and fire safety standards, such as NFPA 14 and the International Building Code (IBC/IFC 905, 2021). Here are key installation requirements:
Standpipe systems require both physical protection and regular maintenance to function correctly during emergencies.